Our Renewable Technologies
Solar Power
Energy Production: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells, providing clean energy for homes and businesses.
Economic Benefits: Reduces energy bills significantly, creates jobs in manufacturing and installation, and boosts local economies through green technology investments.
Environmental Impact: Minimizes reliance on fossil fuels, drastically lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and reduces water usage compared to conventional energy sources.
Philanthropic Initiatives: Solar projects empower off-grid communities by providing reliable energy, enhancing education and healthcare facilities through improved lighting and power supply.
Future Potential: With advancements in solar technology, we expect increased efficiency and lower costs, making solar power accessible to more regions globally.

Wind Power
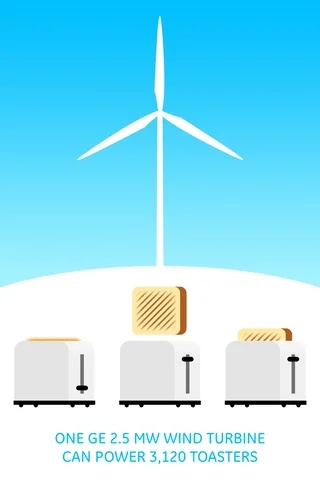
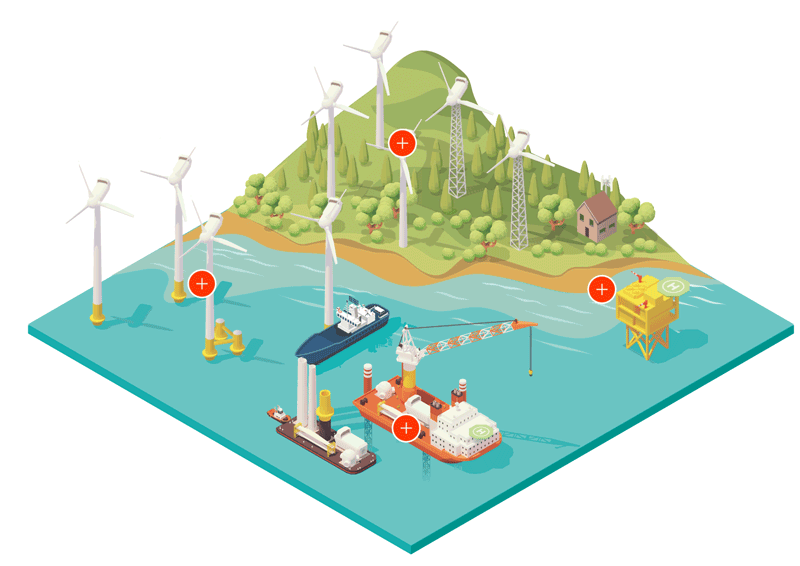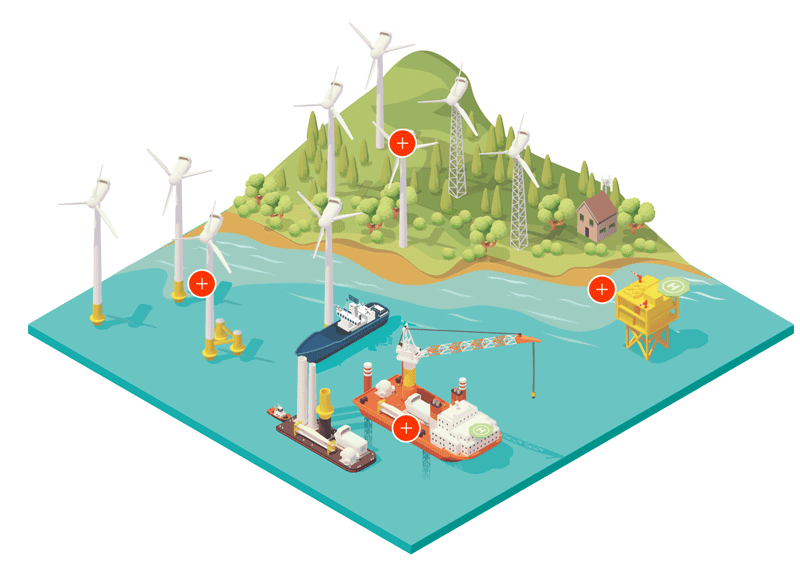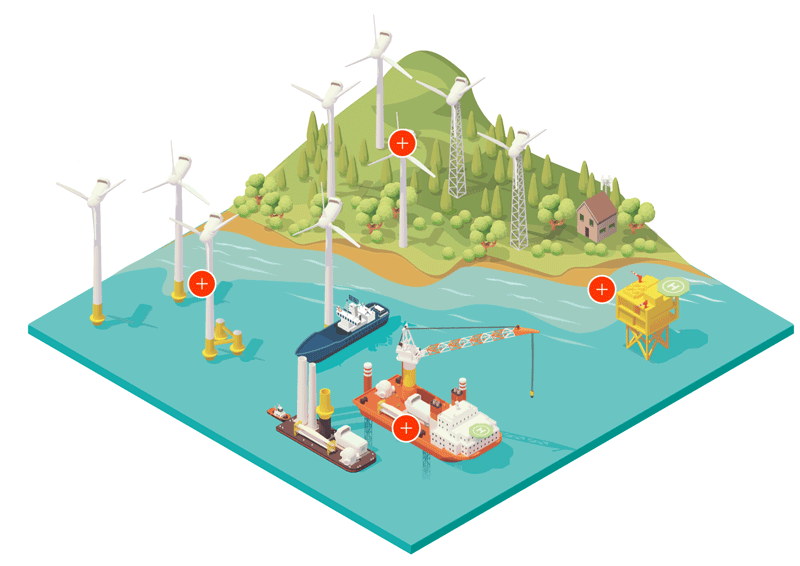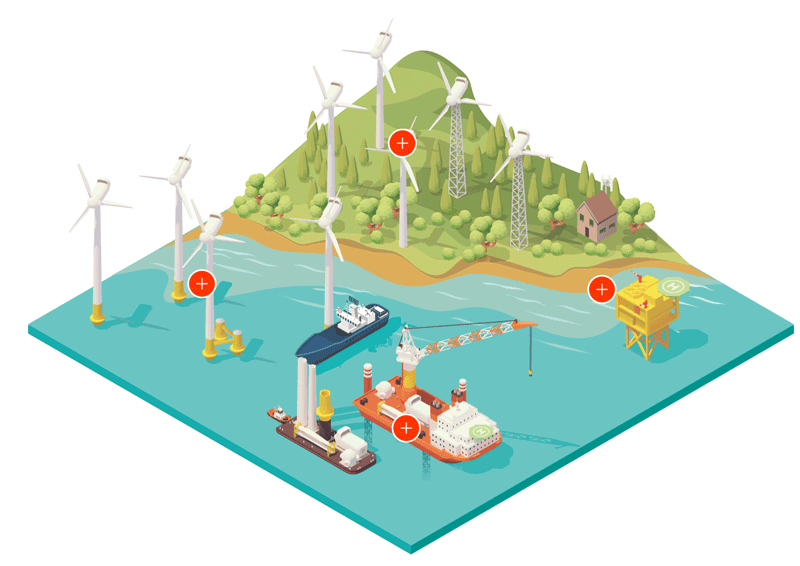
Energy Production: Wind turbines harness wind energy to generate electricity, converting kinetic energy into usable power efficiently.
Economic Benefits: Provides stable job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of wind turbines, contributing to local economic growth.
Environmental Impact: Wind energy is one of the cleanest sources of electricity, producing no emissions during operation and preserving water resources.
Philanthropic Initiatives: Wind farms can support local infrastructure projects, such as road improvements and community development funds, benefiting residents.
Future Potential: Innovations in turbine design and energy storage systems will increase efficiency and expand the viability of wind energy in diverse environments.
Hydropower
Energy Production: Hydropower generates electricity by using the flow of water to turn turbines, making it one of the oldest and most reliable energy sources.
Economic Benefits: Provides low-cost electricity, creates jobs in construction and maintenance, and promotes economic development through affordable energy access.
Environmental Impact: Reduces carbon emissions and contributes to sustainable water resource management, although careful planning is needed to minimize ecosystem disruption.
Philanthropic Initiatives: Hydropower projects can enhance irrigation systems, providing water for agriculture and improving food security in local communities.
Future Potential: Small-scale and run-of-river hydropower projects are gaining traction, offering sustainable energy solutions with minimal environmental impact.